It is a common fallacy that fish is the only source of mercury.
Usually, food can contain Mercury because it exists in the surroundings. Although Mercury can be naturally present in the soil, air and water, the quantity may differ according to the unique features of different locations. For instance, natural sources such as volcanic activity and geological weathering can spread Mercury into the environment. Additionally, human activities like fossil fuel combustion, manufacturing and small-scale gold mining result in environmental pollution which enhances Mercury levels beyond normal limits.
In a study with more than 10,000 pregnant women, researchers showed that seafood contributed to less than half of the mercury obtained from the diet, which in turn contributed about 20% of blood mercury.
Some of the other sources include dental amalgams (dental filling material used to fill cavities caused by tooth decay) and inhalation from the atmosphere.
A person can also be exposed by eating fish and shellfish because some animals absorb low concentrations of mercury from water pollutants. The predator species that live longer and tend to be larger have the most exposure.
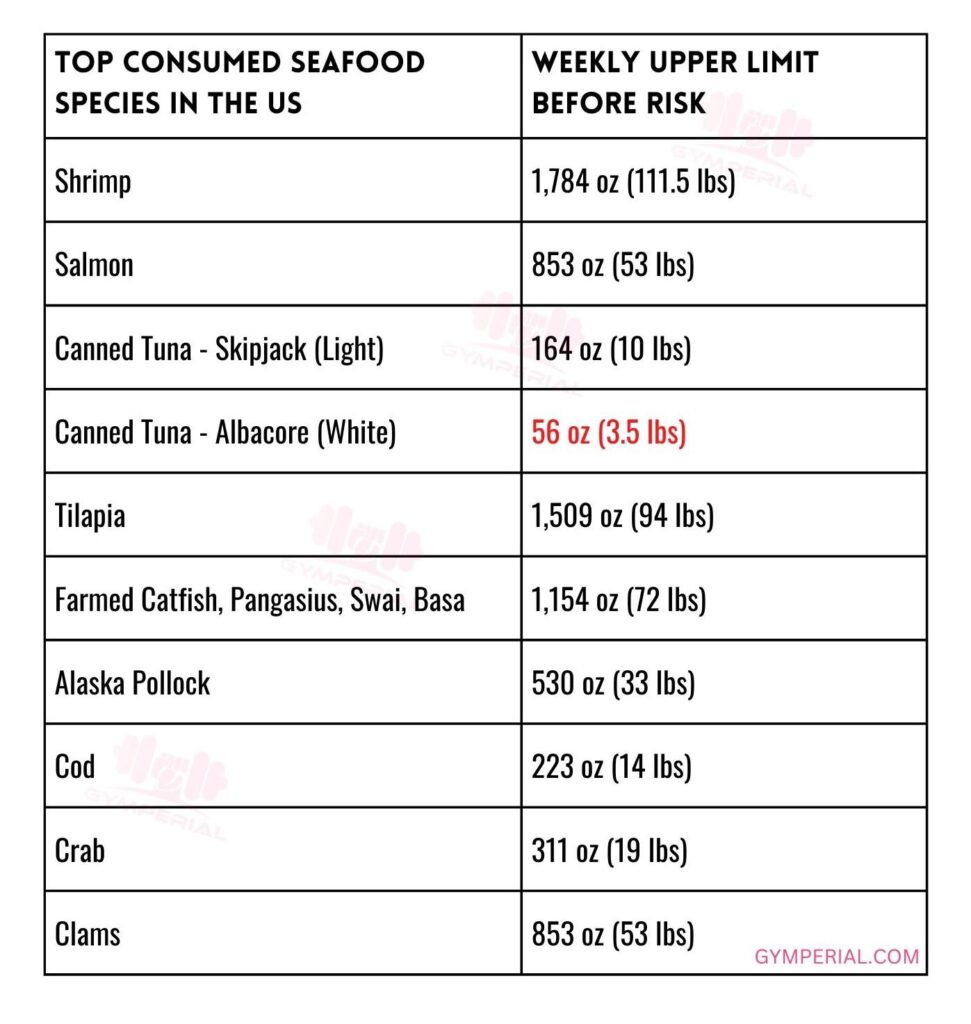
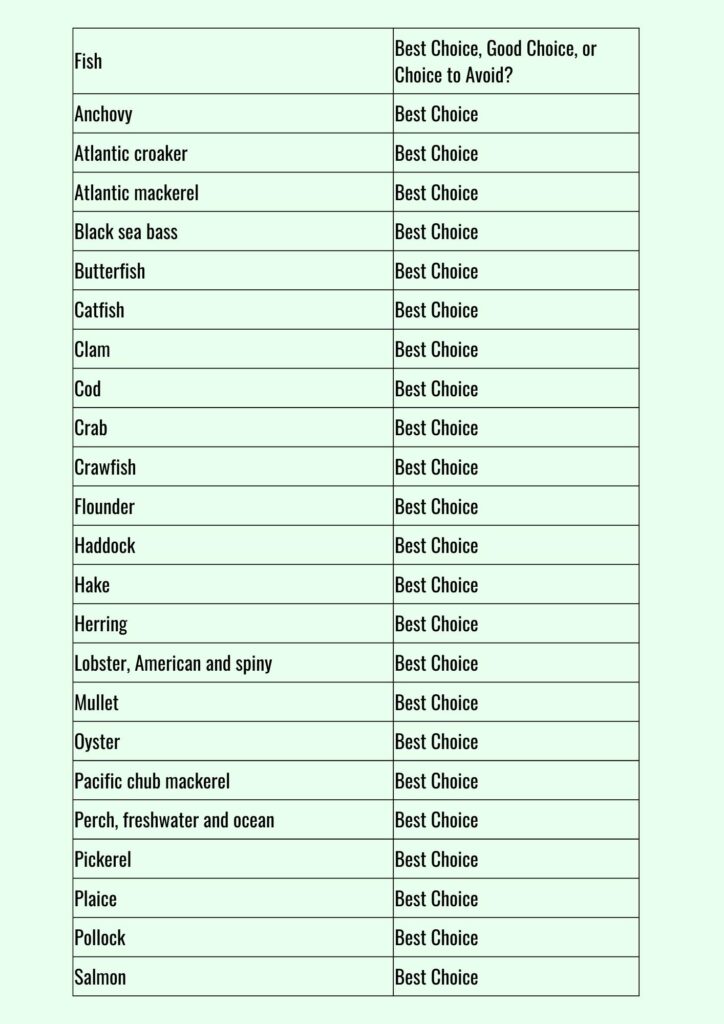
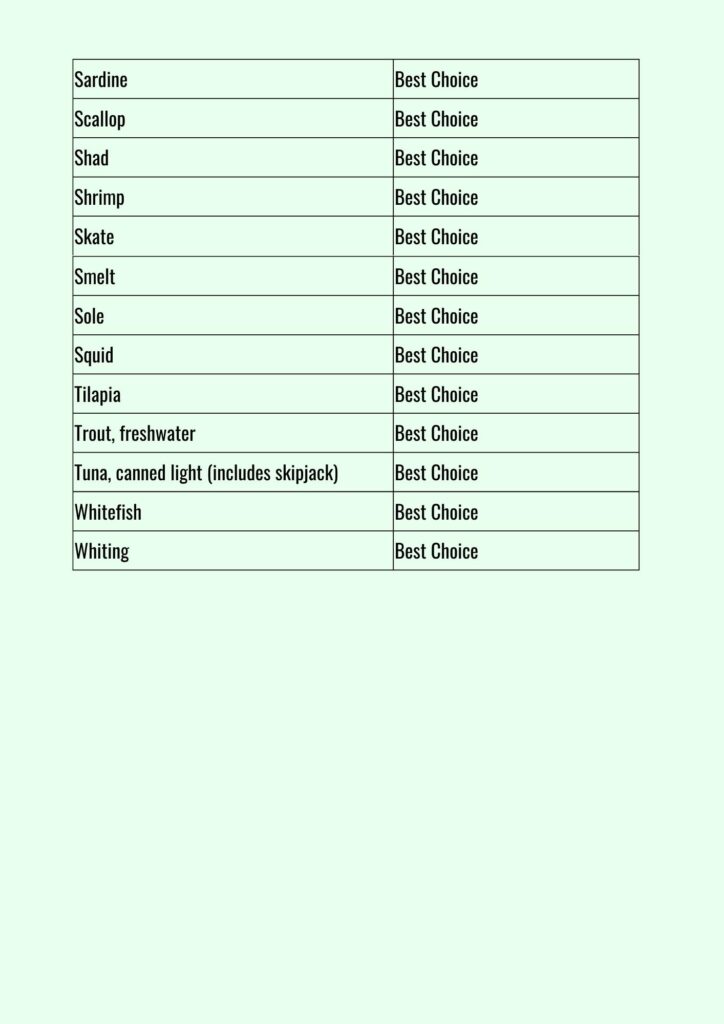
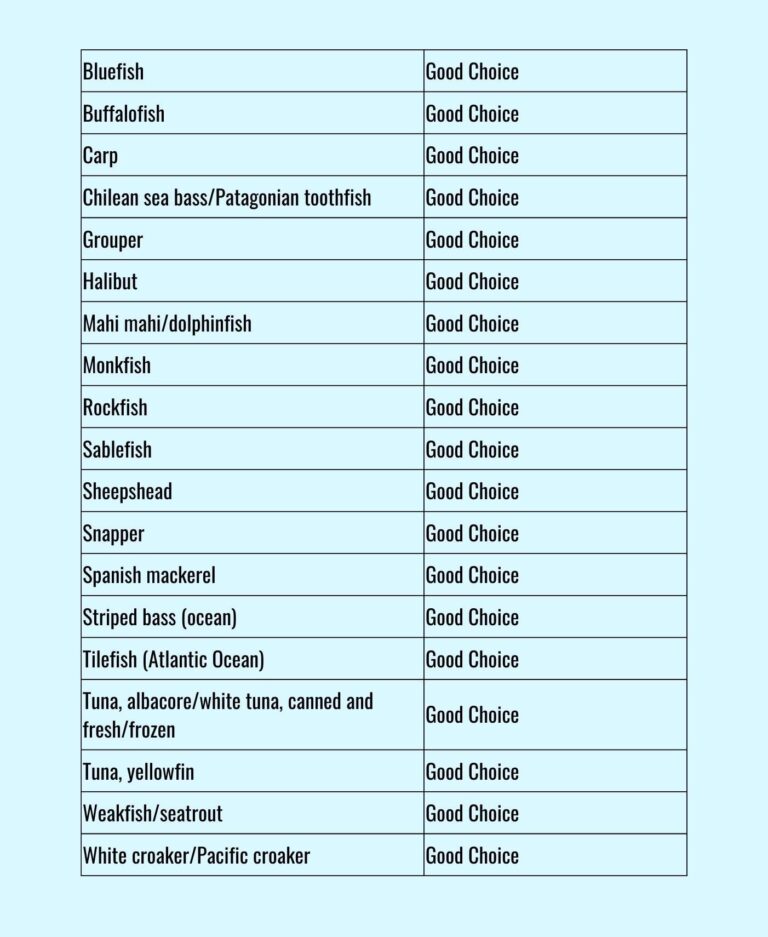
Eating seafood is the primary manner by which individuals in the United States typically encounter mercury, but many varieties of seafood possess levels of mercury that are not harmful to adults. The FDA and EPA have provided guidance on fish selection to aid expectant or nursing mothers, as well as parents and caregivers, in selecting nutritious fish varieties that are low in mercury.
SHOULD I BE CONCERNED ABOUT MERCURY IN FISH?
The recommendations from the Dietary Guidelines for Americans are to eat a variety of seafood at least twice a week to reap the range of nutrients in different types of fish, and for men and women not trying to get pregnant there are no specific species you need to avoid.
In 2019, the FDA and EPA released advice urging pregnant women, breastfeeding moms, and young children to consume more fish and seafood, including all of the most popular seafood in the U.S. from salmon to canned tuna.
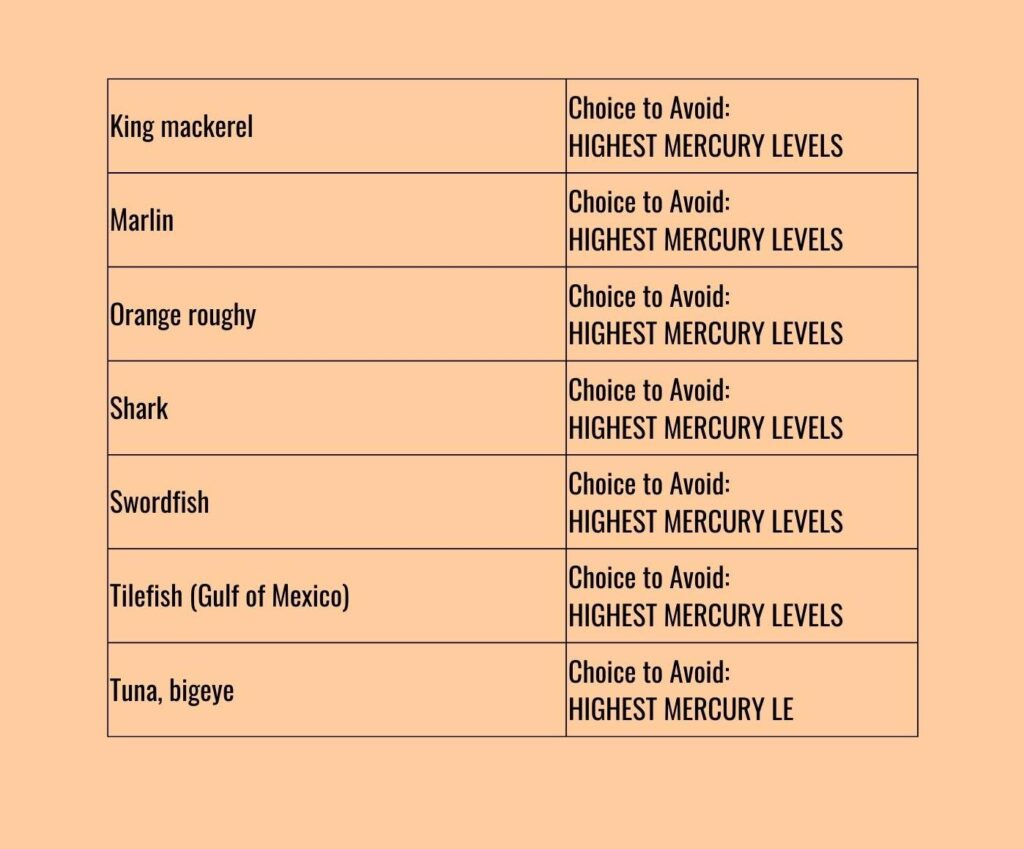
The guidance listed seven fish to avoid during pregnancy due to higher mercury:
🟠 Shark, swordfish, king mackerel, tilefish, bigeye tuna (does NOT include canned tuna), marlin and orange roughy. (2)
Seafood also contains selenium, which is needed for our brain and nervous system to function. The mineral also protects us from mercury by binding to it. Seventeen of the top 25 food sources of selenium in the American diet are types of seafood.
🟢 Yellowfin tuna, halibut and sardines are the best choices for selenium ratio.
In a study looking at fish consumption in pregnant women, there were no adverse effects of prenatal mercury levels provided the mother eats fish, but there was an adverse effect when the mother consumed no fish at all. This study suggests that guidelines need to be simplified and the benefits of fish consumption emphasized more clearly.

***This article will be periodically revised with the latest research findings. To stay informed, please follow along for updates.